Written by “Dr. Javeria Ramzan”, “Muhammad Nasir*”, “Uzair Ahmad” , “Farhan Ilyas” “Department Of Plant Breeding and Genetics,” The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad
Sugarcane is a perennial herbaceous plant of the Gramineae family and is cultivated in various countries. Refined sugar is the primary product obtained from sugarcane juice and sugarcane by-products, i.e., brown sugar, molasses, jiggery, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical applications. Sugarcane juice is widely used in traditional medicine systems to treat a variety of health problems, such as jaundice, dysuria, anuria, and other urinary tract disorders.
The importance of pulp and paper has increased significantly due to exponential population growth, industrialization, and urbanization. Most new product creations for the paper industry use wood fibers to meet pulp and paper needs. The lack of fibrous wood resources and increasing deforestation are associated with over-dependence on wood for pulp and paper production.
Agricultural waste and weedy plant residues can meet the packaging industry’s growing demand for paper as well as hygiene and environmentally friendly products such as paper towels, toilet paper, and disposable cosmetic wipes. Consider that approximately 60% of cellulosic fibers are produced from non-wood materials such as bagasse, etc. Markets in some countries, such as China and India, rely heavily on sugarcane bagasse and wheat straw, which contribute approximately 70% of the requirement for the pulp industry as raw materials.
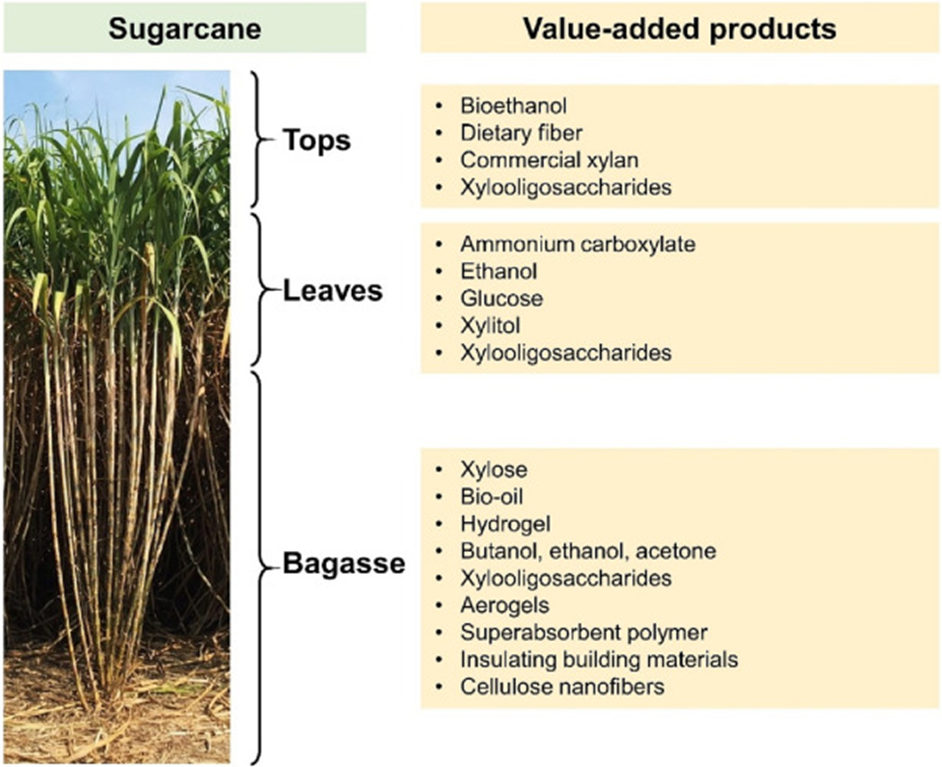
Agricultural residues such as alfalfa and sugarcane bagasse have higher concentrations of cellulose and lower levels of refractory lignin compared to average woody biomass, and also have higher annual growth rates compared to trees. Statistics provided by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) show that global sugarcane production in 2020 will be approximately 1.87 billion tons.
Current global oil resources, fluctuating crude oil prices, and the ecological impact of fossil fuel use have led to growing concerns about the production and use of biofuels. Disadvantages of Biofuels the current of global.
Petroleum resources, fluctuations in crude oil prices, and ecological impacts are considered practical alternatives to FB fuels that can easily and effectively sustain climate change, help enhance energy, and reduce harmful emissions from transportation. Globally, biofuel production continues to increase as crop materials become available. According to people familiar with the matter, biofuel production was 59 million tons of oil equivalent (M-Toe) in 2010 and 96 M-Toe in 2019. It is expected to increase to 98 million tonnes by 2022 and increase year by year.